Thesis by Joudy Dankar: « Mechanistic study of the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 over Pt/TiO2 using an operando FTIR approach »
The photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to “C1/C2 solar fuels”1 is an attractive conversion reaction since it has the advantage of eliminating this greenhouse gas while providing a usable product.
However, despite extensive research efforts, the level of CO2 conversion remains very low, even for the most active catalysts on the market, and the reaction mechanisms involved is still poorly understood.
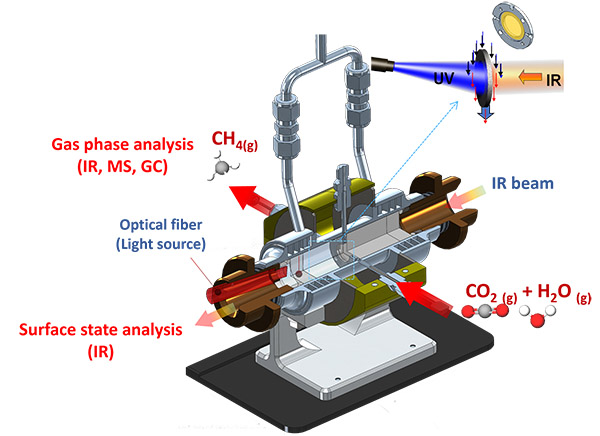
In order to remedy this, this PhD research focused on the study of a model Pt/TiO2-type photocatalytic system. For the purpose of the study, an operando methodology2 was deployed combining several techniques:
- infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to characterize the irradiated catalyst surface;
- mass spectrometry and gas phase chromatography to analyze the gaseous effluents generated.
This approach made it possible to determine correlations between the structure/surface of the catalyst and its activity. In addition, various “ex situ” analyses were carried out, including Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), X-ray Photoelectron Spectrometry (XPS), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), as well as the processing of spectral data using a chemometric approach (MCR-ALS) and the use of isotopes in specific operando FTIR measurements (13CO2, D2O). This made it possible to determine the factors governing the photocatalytic activity of the system studied.
The information obtained underline in particular: i) the importance of the presence of carbon impurities on the catalyst surface (leading to an overestimation of activity) [1] ii) the beneficial effect of cycled irradiation conditions [2] and iii) the central role of acetate species in the CO2 photoreduction reaction [3].
These observations reveal the complex dynamics involved in the photocatalytic reduction of CO2. They also provide a potential lever for improving the performance of the photocatalyst for the reaction via modulation of the surface chemistry/properties and/or reaction conditions.
1- Syngas, methane/methanol, formic acid, C2 + liquid fuels.
2- In reaction conditions, with monitoring of changes and products.
References:
-
Dankar, Joudy; Pagis, Céline; Rivallan, Mickael; El-Roz, Mohamad, Operando FTIR study of the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in the presence of water vapor over Pt/TiO2: on the role of surface residual C-species, Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2023,7, 2819-2823.
>> DOI : https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SE00227F
-
Dankar, Joudy; Rouchon, Virgile; Pagis, Céline; Rivallan, Mickael; El-Roz, Mohamad, Exploring the effect of the reaction conditions on the mechanism of the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 in the vapor phase over Pt/TiO2: an operando FTIR study, Inorg. Chem. Front., 2023,10, 7155-7166.
>> DOI : https://doi.org/10.1039/D3QI01758C
-
Dankar, Joudy; Rouchon, Virgile; Rivallan, Mickael; Pagis, Céline; El-Roz, Mohamad, Evidence on C–C Coupling to Acetate as Key Reaction Intermediate in Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2 over Pt/TiO2, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 32, 42210–42220.
>> DOI : https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.4c07256
Scientific contact: mickael.rivallan@ifpen.fr





