01.07.2019
15 minutes of reading
 Porous media have in common to develop a large interface that divides the space with a varying degree of complexity, potentially with hierarchical structuring. Such environments are central to IFPEN’s research on geological formations and certain industrial materials.
Porous media have in common to develop a large interface that divides the space with a varying degree of complexity, potentially with hierarchical structuring. Such environments are central to IFPEN’s research on geological formations and certain industrial materials.
The thermodynamic, dynamic and rheological properties of the fluids present in the porous network are strongly influenced by the nature of interfacial interactions (wettability and adsorption) and by the degree of confinement of the pore space. This dual dependency makes it possible to cover a rich phenomenology of behaviors associated with molecular adsorption, thermodynamic phase diagrams, micro or even nanorheology of confined fluids, more or less complex (foams, emulsions, etc.), and with their transport and reactivity. For the latter field, searching optimized reaction conditions remains a real challenge.
This issue presents recent research in this rich and dynamic field, in which the dual top-down and bottom-up approach is very promising for crossing time and space scales, from macroscopic through to nanocontainment, a research area still full of surprises.
I hope you enjoy reading this issue,
Pierre Levitz,
CNRS - Sorbonne University and Expert for IFPEN's Scientific Board
 See the PDF of the letter (1.4 Mo)
See the PDF of the letter (1.4 Mo)
Carbon steel in self-defense mode against corrosion
Carbon or low-alloy steel corrosion, by aqueous media containing CO2, hampers the development of numerous technologiesa f
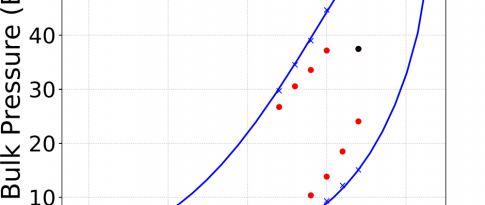
Foam rheology in porous media
For processes involving gas injection, such as enhanced oil recovery (EORa) and CO2 storage operations, the
Phase equilibria in confined media
In many geological reservoirs, pore size distribution is highly heterogeneous (from 2 to 50 nm).
What percentage of free compounds in porous media?
The energy mix required to satisfy global needs will include fossil hydrocarbons for some time to come.
Adsorption, a key factor for geological storage
Low permeability geological layers, already known within the context of oil exploration, are once again becoming a focus of inter
For xylene separation, hierarchy is not all bad
The three xylenea isomers are each employed in numerous growth market applications (polymers, plastifiers